Introduction to High Voltage
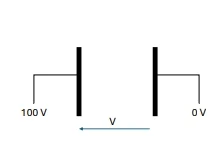
- Voltage is the Electric Potential difference between two points.
- If the voltage is on or above 1000 V ( 1 kV), we called it High Voltage.
Types
of High Voltages
Alternating Current (AC)
o High Voltages High Voltage AC
(HVAC): 1000 V (1 kV) and up to 1,000,000 (1000 kV)
o Ultra-High Voltage AC (UHVAC): 1,000,000 (1,000 kV)
Direct Current (DC)
o High Voltages High Voltage DC
(HVDC): 1000 V (1 kV) and up to 1,000,000 (1000 kV)
(Some
classifications use 1.5 kV instead of 1 kV)
o Ultra-High Voltage DC (UHVDC): 1,000,000 (1,000 kV) and above
1.
Infrastructure
to Handle High Voltages
·
HV
systems require specialized infrastructure, such as insulated transmission
lines, substations, and switchgear to manage high voltage levels safely.
·
The
construction and maintenance of these facilities demand high costs and
expertise.
2.
Required
Specific Equipment
·
High
voltage applications need specialized transformers, circuit breakers,
insulators, and conductors designed to withstand extreme voltages.
·
Testing
and maintenance equipment must also be suitable for HV conditions.
3.
Protection
and Monitoring
·
High
voltages pose a higher risk of faults (such as insulation failure, arcing, and
corona discharge).
·
Advanced
protection relays, surge arresters, and SCADA-based monitoring systems are
required to detect and mitigate faults.
4.
Safety
·
HV
systems are extremely dangerous, requiring strict safety measures, including
proper grounding, isolation, and personal protective equipment (PPE).
·
Workers
must be trained in HV safety protocols to avoid electrical hazards like shocks
and arc flash incidents.
5.
Clearance
·
Adequate
clearance distances must be maintained for HV power lines and equipment to
prevent flashover and unintended contact.
·
Right-of-way
management is necessary to avoid obstructions (e.g., trees, buildings) near HV
lines.
High
Voltage Equipment
High
Voltage Transformers (HV Transformers)
High-voltage
(HV) Transformers are critical components in electrical power systems. They are
used to raise or lower voltage levels for efficient transmission and
distribution. They ensure that power is transmitted over long distances with
minimal losses and safely delivered to consumers.
Types
of High Voltage Transformers
- Power Transformers
- Used in transmission networks
to step up voltage for long-distance transmission and step-down voltage
for distribution.
- Operates at voltages above 33
kV and has high power ratings (up to 1000 MVA).
- Instrument Transformers
- Current Transformers (CTs):
Reduce high currents to measurable levels for meters and protection
systems.
- Voltage Transformers (VTs) or
Potential Transformers (PTs): Step down high voltages for safe
measurement and relay operation.
- Distribution Transformers
- Steps down voltage for local
distribution to homes and industries (e.g., from 11 kV to 400V).
- Lower power ratings compared
to power transformers (up to 5 MVA).
- Autotransformers
- Uses a single winding to
transfer power with a common section for both primary and secondary.
- More compact and efficient
than conventional transformers but with limited isolation.
- Phase-Shifting Transformers
(PSTs)
- Controls power flow between
different grid sections by adjusting phase angles.
- Helps in load balancing and
preventing overloading in transmission networks.
- HVDC Converter Transformers
- Used in high-voltage direct
current (HVDC) systems to convert AC to DC and vice versa.
- Designed to handle high
voltages and harmonic stresses
High
Voltage Equipment: Bushings & Insulators
What
are HV Bushings?
Bushings
are insulating components that allow electrical conductors to pass
through grounded barriers (e.g., transformer tanks, circuit breakers,
switchgear) without causing short circuits.
Types
of HV Bushings
- Oil-Impregnated Paper (OIP)
Bushings
- Uses paper impregnated with
insulating oil for electrical insulation.
- Commonly used in power
transformers and circuit breakers.
- Requires regular oil
maintenance and monitoring.
- Resin-Impregnated Paper (RIP)
Bushings
- Insulation is achieved using paper
impregnated with epoxy resin.
- No oil, so it has better
environmental and fire safety.
- More durable and maintenance-free
compared to OIP bushings.
- Resin-Bonded Paper (RBP)
Bushings
- Similar to RIP but uses a different
resin bonding technique.
- Used in medium voltage
applications.
- Capacitive Graded Bushings
- Contains multiple capacitive
layers to distribute voltage evenly, reducing electrical stress.
- Used in EHV and UHV
applications (400 kV and above).
What
are HV Insulators?
HV
insulators prevent current leakage by supporting conductors and
isolating them from the ground or structures.
Types of HV Insulators
Types
Based on Application
- Pin Insulators → Used for lower
voltage distribution lines.
- Suspension Insulators → Used
in HV transmission lines (above 33 kV).
- Strain Insulators → Supports long
spans and mechanical loads in transmission systems.
- Post Insulators → Used in substations
and switchgear.
High
Voltage Circuit Breakers (HVCBs)
High
Voltage Circuit Breakers (HVCBs) are essential components in power systems for
interrupting high voltage electrical currents under normal and fault
conditions. They protect electrical grids by isolating faulty sections,
preventing damage to equipment, and ensuring system stability.
Types
of High Voltage Circuit Breakers
- Air Circuit Breaker (ACB)
- Uses compressed air to
extinguish the arc.
- Mainly used in medium voltage
applications but also found in some HV systems.
- Requires frequent maintenance
due to arc chutes and moving parts.
- Oil Circuit Breaker (OCB)
- Uses insulating oil as both
an arc-extinguishing medium and an insulator.
- The oil absorbs the arc
energy, vaporizing and creating a high-pressure bubble to extinguish the
arc.
- Requires regular oil
replacement and maintenance to remove carbon deposits.
- SF₆ Circuit Breaker (Sulfur
Hexafluoride)
- Uses SF₆ gas as an insulating
and arc-quenching medium.
- Offers excellent dielectric
strength, fast operation, and minimal maintenance.
- Widely used in extra high
voltage (EHV) and ultra-high voltage (UHV) systems.
- Vacuum Circuit Breaker (VCB)
- Uses vacuum as the
arc-extinguishing medium.
- The arc is extinguished
quickly due to the absence of ionized particles.
- Suitable for medium voltage
but limited for HV applications.
- Hybrid Circuit Breakers
- Combines the advantages of SF₆
and vacuum technologies.
- Faster operation and reduced
environmental impact.
- Used in smart grid and
high-speed switching applications.

0 Comments